4. UNIVERSAL POTENTIAL ENERGY of
REPULSING
This book is saturated with criticism of known physical notions and
theories. Specially it concerns to a modern physics.
But it is more logical to a critic to start from classic notions.
At even and rectilinear motion of a body with speed V its kinetic energy
is peer:
Wk = mV2/2 (1).
That the body has the indicated energy, instead of any another is easy
for testing by experiment. Let body will get in the calorimeter (device for
measurement of a quantity of heat) and we shall determine, that at a stop of a
body the allocated thermal energy in accuracy is peer to former kinetic energy
on an equation (1), instead of to what to another.
Let's consider rotation of a body on a circumference of radius r with
speed V. Apparently, that the energy of this body too will be determined by
expression (1). It is easy for testing by cutting off a thread, which one
retains a body on a circumference. The body will become to move uniformly and
rectilinearly with the same speed V, т.е will gain kinetic energy Wk. We link to kinetic energy
capacity of a body unrestrictedly to leave from view point. But the body,
rotated on a circumference, does not leave anywhere and remains on same spacing
interval from center of rotation, i.e. fixed concerning this center. This
property of potential energy of a body: to have capacity to be turn intoed kinetic energy, stay put. Is linkable a body
with center of rotation by a rod on which one a body can be displaced in a
radial direction. To move up it to center, it is necessary to expend energy,
and at deleting from center it is necessary a body to hold, since the energy is
allocated. As a whole, at anyone movements and return of a body in initial
point if to neglect friction, the energy of a body start initial value, that is a consequent of an energy conservation law. It too property of potential energy. If we
shall raise and to lower shipment on a miscellaneous altitude, we shall come to
the same conclusion. Thus, any body at motion on a curvilinear
trajectory has universal potential energy of repulsing from center of curvature
trajectory. For the greater clearness of this problem we shall consider motion
of a space body m on an elliptical trajectory around of a central body M, which
one is shown on a figure 1.
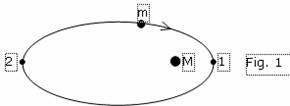
In a point 1 pericentre of orbit (if M - Sun, this point is called as a
perihelion) body m has maximum speed, therefore greatest possible potential
energy of universal repulsing and bound with it maximum centrifugal force. At
the same time, spacing interval up to a central body in this point is minimum
also customary potential energy, bound lift bodies m on a definite altitude
from a central body M also is minimum. The energy conservation law requires, that the sum of universal potential energy of
repulsing and customary potential energy at linear deleting of one body from
another should be a constant. The zerolevel of customary potential energy can
be accepted arbitrary, therefore in a point 1 it is possible to consider it to
equal zero point. In a point 2 apocenter of orbit (if M - Sun, this point is
called apogee of orbit) body m has minimum speed, but maxheight above a central
body М. The sum of universal potential
energy of repulsing and customary potential energy (attraction) will be peer to
potential energy of repulsing a point 1, if in it energy of attraction
conditionally we shall accept for zero point. Thus, at motion of a space body
on elliptical orbit the sum of universal potential energy of repulsing and
potential energy of attraction always remains to a constant. Potential energy
of repulsing conditionally consider positive, and
potential energy of attraction - negative. Certainly, it is conditionality,
bound that these kinds of energy have opposite properties. It would be
possible, on the contrary, potential energy of attraction to consider positive,
but in this case there is a disadvantage at dialogue. It is possible customary
table to call «object», but then it is necessary to everyone to explain, that
your object is completely identical to our table. On the basis of above-stated,
we can record the main equation of motion of a body on a curvilinear trajectory
in a potential field (electrostatic or gravitational) for which one
characteristicly, that the work of movement of a charge (electrical or
gravitational) on a closed loop is peer to zero point. This equation looks like
this:
E(tie)= W(rep) - W(att)
(2),
where E(tie) - bond energy of two interacting bodies, W(rep)
- universal potential energy of repulsing of these bodies, and W(att)
- potential energy of attraction of bodies.
On indefinitely large spacing interval of any interplay between bodies
there is no, therefore E(tie), W(rep) and W(att)
everyone is peer to zero point, accordingly, and their sum (total energy) also
is peer to zero point. Such it also remains in any point of any trajectory on
demand of an energy conservation law. Pay attention, that
we here not mention at all kinetic energy of a body. It would appear from
potential energy, when the body will confront with an encumbrance, but such
case we here not envision.
To concretize an equation (2) for a case electrostatic or gravitational
interaction, we shall decrypt in (2) values W(rep)
and W(att).
Energy of attraction of two unlike electric charges q1 and q2
is determined by a Coulomb's law:
W(att.e)=(q1×q2)/r (3),
where r - spacing interval between charges.
Energy of attraction between two gravitational charges (some masses m1
and m2) is determined by a law of universal gravitation of a
W(att.g)=(G×m1×m2) /r (4),
where G - gravitational constant.
Equation (2) we shall apply to bodies of small mass driving on orbit
around of massive bodies. It is most relevant in practice a case suitable for
the description of an electron motion around of a nucleus or satellites around
of a massive central body (of the Sun or planets). In this case it is possible
to consider a central massive body fixed (though as a matter of fact both
bodies are gyrated around of common center of gravity of a system), differently
calculations considerably become complicated in damage to comprehension of the
essence of process.
W(rep) in considered interplays is identical (is universal)
and numerically is peer to «kinetic» energy of a body on orbit:
W(rep)=mV2/2 (5).
But we are interested by change of universal potential energy of
repulsing depending on a radius of gyration, instead of speed of a body.
Therefore we shall take advantage of a principle of conservation of moment of
momentum:
L=mVr (6), where L=const.
Let's substitute (6) in (5) instead of V:
W(rep)=L2/(2mr2) (7).
Now, in view of equations (7), (3) and (4), the equation (2) can be
written to an obvious kind for electrostatic interplay:
E(tie.e)=L2/(2mr2)-(q1×q2)/r (8)
And for a gravitational interaction:
E(tie.g)=L2/(2mr2)-(G×M×m)/r (9).
The graph of change of bond energy of interacting (attracted) bodies is
shown on a figure 2.
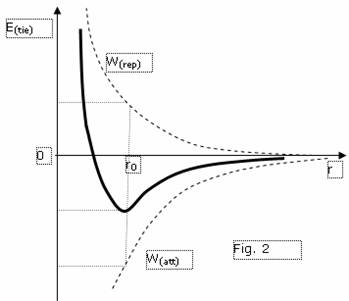
From equations (8) and (9) it is visible, that with decreasing of spacing
interval up to a central body (arranged in a point 0) potential energy of
universal repulsing are augmented more abruptly (in a denominator a square of
spacing interval) than energy of attraction (in a denominator spacing interval
in the first degree) therefore summary curve for bond energy will have a
minimum (potential well). This condition of stable equilibrium and any
elliptical orbits early or late are transformed in circumferential with radius
r0 at the expense of the gradual forfeit of exuberant energy to an
equal difference between energy of repulsing and bond energy. From a figure 2
also it is possible to note, that the energy of repulsing is peer in steady
position to bond energy and twice less energy of attraction (this conclusion in
physics is called as a virial theorem).
At invariable mass of a body its product Vr remains to a constant (Vr=a), then (6) it is
possible to copy so:
L=ma (10),
and the equations (8) and (9) will accept a kind:
E(tie.e)=ma2/2r2 - (q1×q2)/r (11),
E(tie.g)=ma2/2r2 - (G×M×m)/r (12).
Equations (11) and (12) is applicable for practically relevant cases:
the rotation of an electron with a charge е and mass me around of a
nucleus having the charge Z and some space body in mass m, revolving around of
a central massive body M. The finding of a position of a potential well for
these cases requires applying differentiation of equations (11) and (12),
therefore we shall put at once end results for r0 - spacing interval
from a central body to the bottom potential wells:
r0=(mea2)/(Ze2) (13) - for atom
both
r0=a2/GM (14) - for a space system.
It is understandable, that values a=Vr for an electron and
space body miscellaneous.
If to substitute (13) and (14) in the applicable equations (11) and (12),
we shall discover electron-binding energy with a nucleus or (for example) of
Earth with the Sun:
E(tie.e)=-(Ze2)2/(2mea2) (15).
E(tie.g)=-(G2M2m)/2a2 (16).
The negative values of bond energy demonstrate (conditionally) that
energy, which one should be expended to eliminate a rotated body in perpetuity.
It is interesting to count up bond energy of the Earth with the Sun.
Orbital velocity of the Earth of 30 kms/sec=3×106 cm/sec,
spacing interval up to the Sun 1.5×1013 cm, therefore, a for the Earth is equal
4.5×1019 cm2/sec. Gravitational constant 6.7× 10-8 dynes×cm2×g-2, Mass of
the Sun 2×1033 g, mass of the Earth 6×1027 g.
Substituting all these values in the formula (16) we shall discover bond
energy: 2.7×1040 ergs. True bond energy it is a little
less, since orbit of the Earth not circumferential, and elliptical, i.e. the
Earth has some exuberant energy, which one has not lost yet neck and crop.
Here it is necessary to note, that official physics does not know about
existence of a potential well at electrostatic and gravitational interaction.
Instead of a pit it has potential abyss and electrons should drop on a nucleus
of atom, and satellites - on a central body. Why they do not drop official
science explains by a rather artful way, which one here we shall not esteem,
the nature is more simply, than the official scientists think of it. Here it is
necessary to pay attention the reader to that circumstance, that the official
scientists somehow explain any phenomena, because receive for it the salary. What
price of these explanations you will understand, by reading the book. Will
appear, that the majority of explanations not only is not explained observed
phenomena, but also enter the reader in fallacy by different methods not
compatible with the present science.
Else about motion of a body on a
circumference.
This
motion is, as though, porch physics and by not understanding its essence cannot
be gone into rooms.
The
orthodoxes in this problem have got confused also others have complicated and prolong
to create tangle in heads of millions schoolboys all over the world. Now this tangle in each head.
1.
Power aspect of a problem.
At
motion on a circumference on a body the attractive force to center of rotation
acts and the centrifugal force of inertia acts (orthodoxes it name as dummy
force to distinguish the stepdaughter from the native daughter - centripetal
force). The forces these are always balanced at steady
circular motion,
therefore of resultant force is peer to zero point and does not cause on
the second
2.
Power aspect of a problem.
Each
time cut off a thread on which one is bound a rotated body, we are convinced,
that any energy is transformed into this moment in kinetic energy of a free
body, and the law of conservation of angular momentum L=mVr is strictly
executed, therefore body is gone on tangent to a former trajectory. As from
time of creation of a world the rotated body was not moved anywhere, its energy
we shall consider as universal potential energy of repulsing. In the given
problem we have not dynamics, and clean statics. The force in this case is of
derivative POTENTIAL energy on spacing interval. Really, by recording potential
energy electrostatic or gravitational interaction of two bodies and
differentiated on radius, we shall receive a Coulomb's law or law of world-wide
attraction of a
E=mV2/2,
V2=L2/m2r2, E=L2/mr2,
dE/dr=-mV2/r. We have received "law of inertia" for a
rotated body.